The 19th chapter of Madhava Nidana deals with Daha Nidana which deals with Diagnosis regarding the burning sensation in the body is. A burning sensation is a type of pain that’s distinct from dull, stabbing, or aching pain. A burning pain can be related to nerve problems.
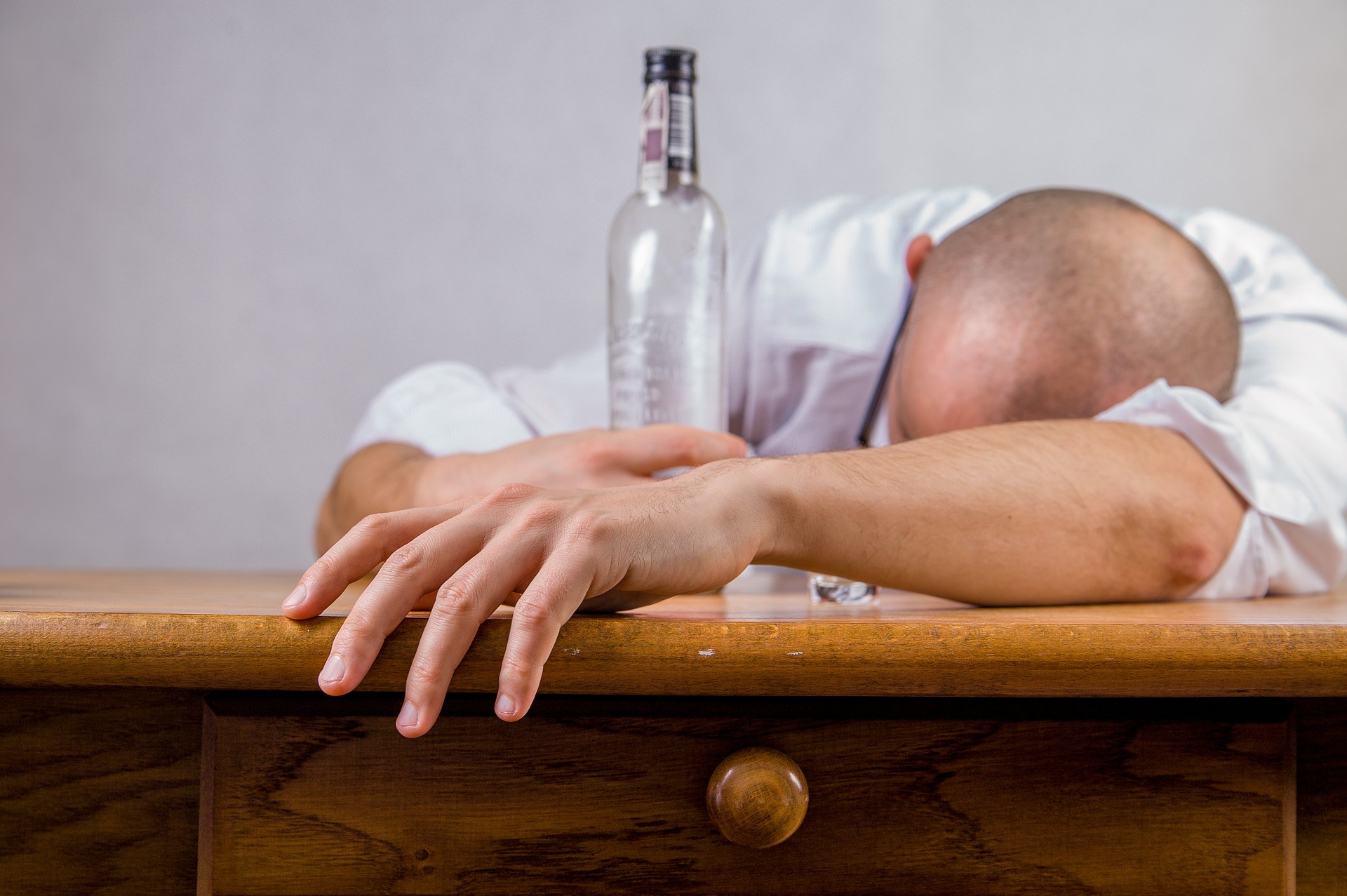
Chapter 18 – Panatyaya, Paramada, Panajirna and Panavibhrama Nidanam (Alcoholic intoxication)
The 18th chapter of Madhava Nidana deals with Panatyaya, Paramada, Panajirna and Panavibhrama Nidanam (Alcholic intoxication). Acute alcohol intoxication is a condition associated with drinking too much alcohol in a short amount of time. It’s also called alcohol poisoning. Alcohol intoxication is serious. It affects your body temperature, breathing, heart rate, and gag reflex. It can also sometimes lead to coma or death.
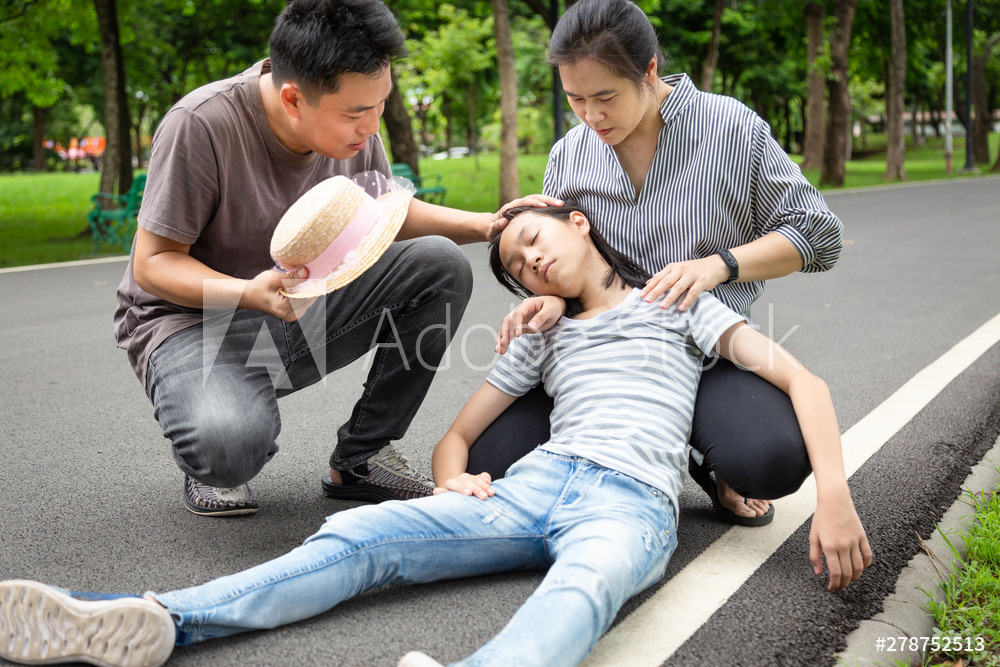
Chapter 17 – Murccha, Bhrama, Nidraa, Tandra, Samnyasa Nidanam
The 17th chapter of Madhava Nidana deals with Murccha, Bhrama, Nidraa, Tandra, Samnyasa which is Fainting, Giddiness, slumber, stupor and loss of consciousness. Fainting is when you lose consciousness for a short time. It’s caused by a sudden drop in blood flow to the brain. A fainting episode usually lasts a few seconds or minutes, then the person wakes up and returns to normal.
Chapter 16 – Trshna Nidana
The 16th chapter of Trshna Nidana that is it deals with the diagnosis of thirst. Thirst is normally just the brain’s way of warning that you’re dehydrated because you’re not drinking enough fluid. But excessive and persistent thirst (known as polydipsia) could be a sign of an underlying problem such as diabetes.
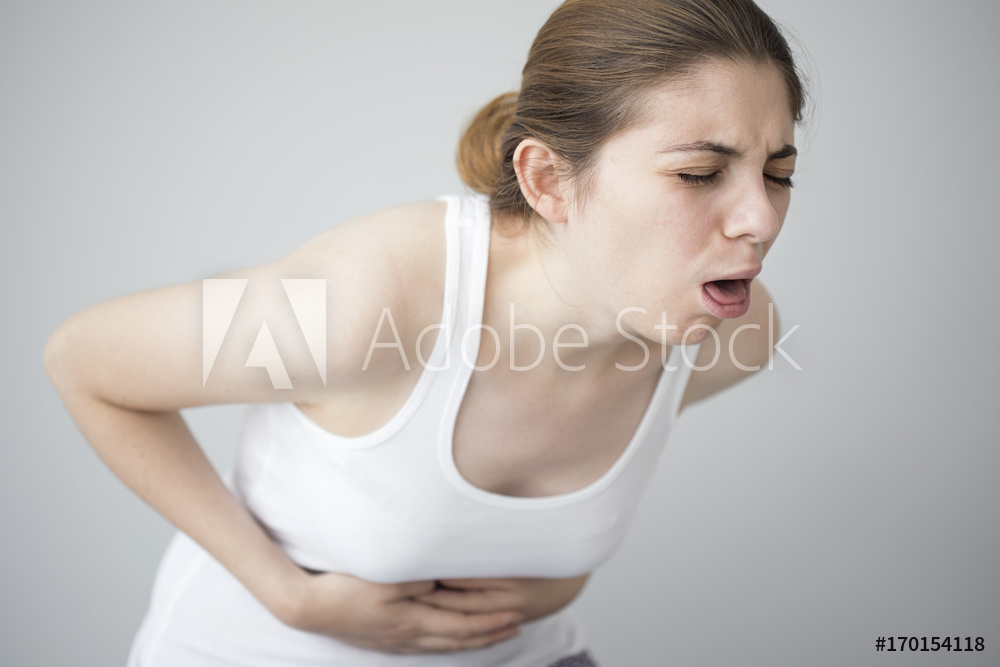
Chapter 15 – Chardi Nidana
The 15th chapter of Madhava Nidana deals with Chardi Nidana i.e. vomiting. Vomiting, or throwing up, is a forceful discharge of stomach contents. It can be a one-time event linked to something that doesn’t settle right in the stomach. Recurrent vomiting may be caused by underlying medical conditions.
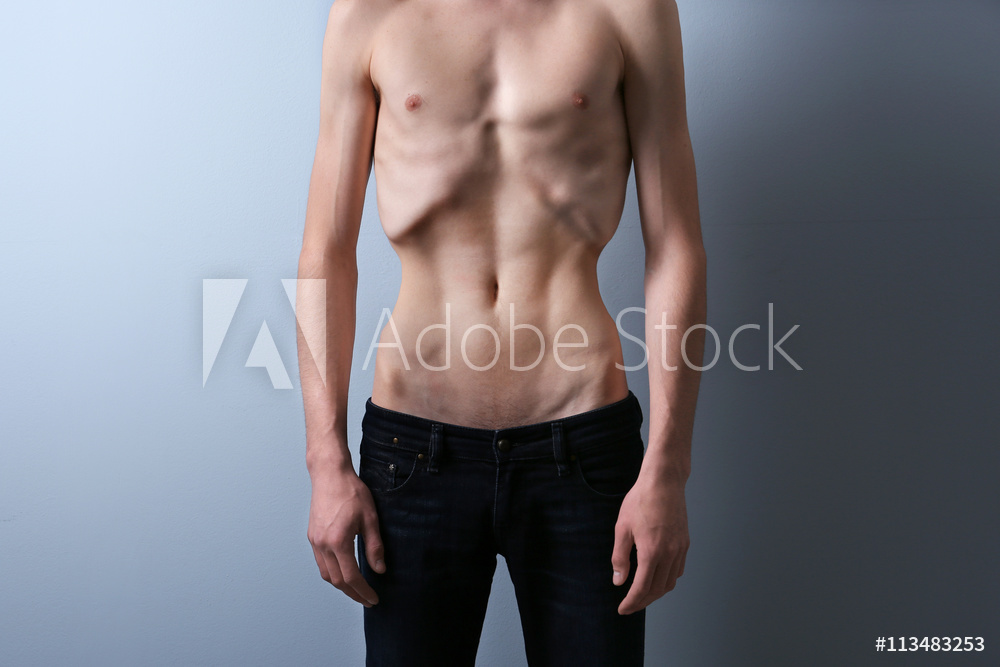
Chapter 14 — Arochaka Nidana
The 14th chapter of Madhava Nidana is Arochaka Nidana which is a detail explanation of Anorexia. Anorexia nervosa — often simply called anorexia — is an eating disorder characterized by an abnormally low body weight, an intense fear of gaining weight and a distorted perception of weight. People with anorexia place a high value on controlling their weight and shape, using extreme efforts that tend to significantly interfere with their lives.