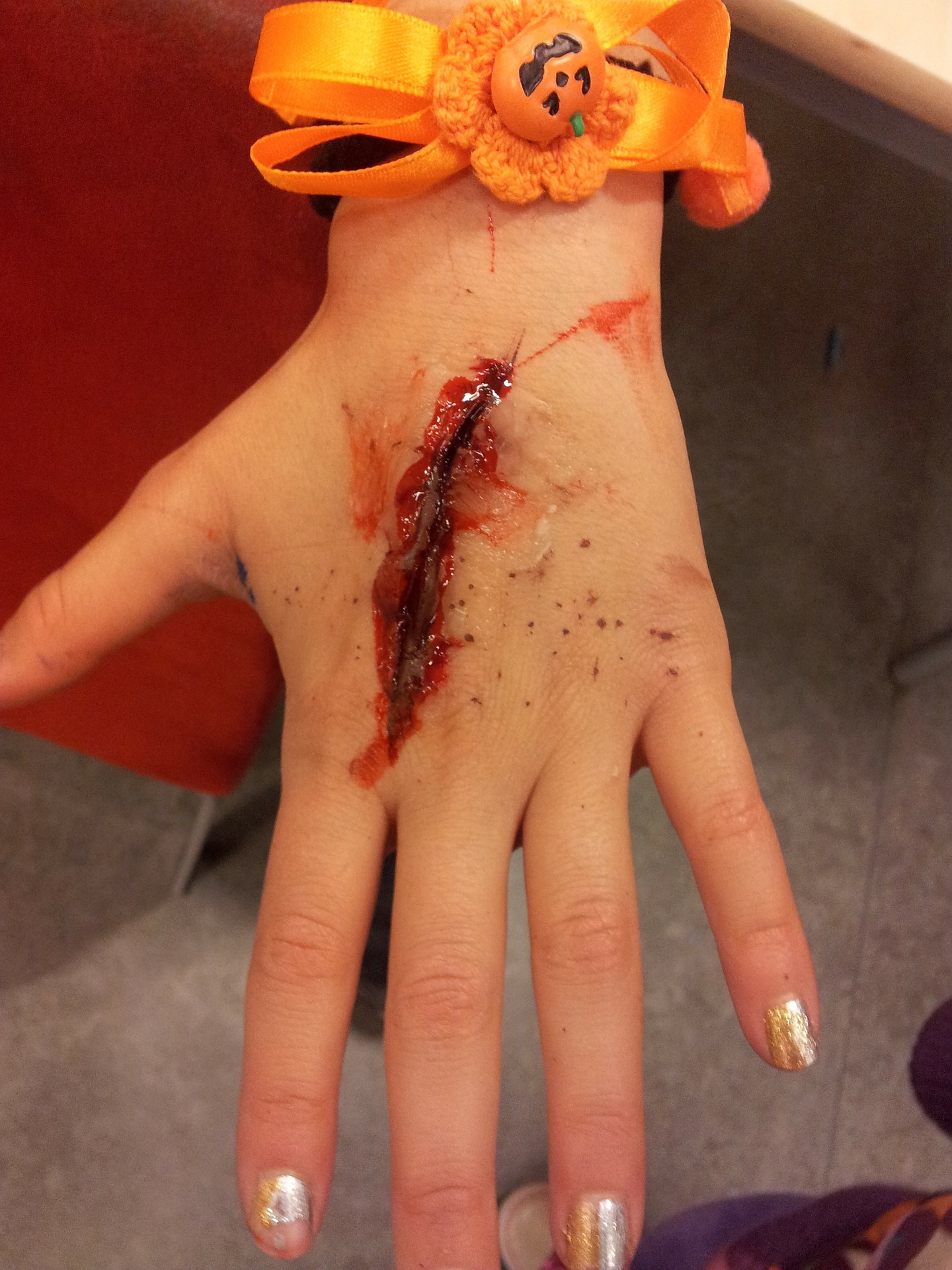
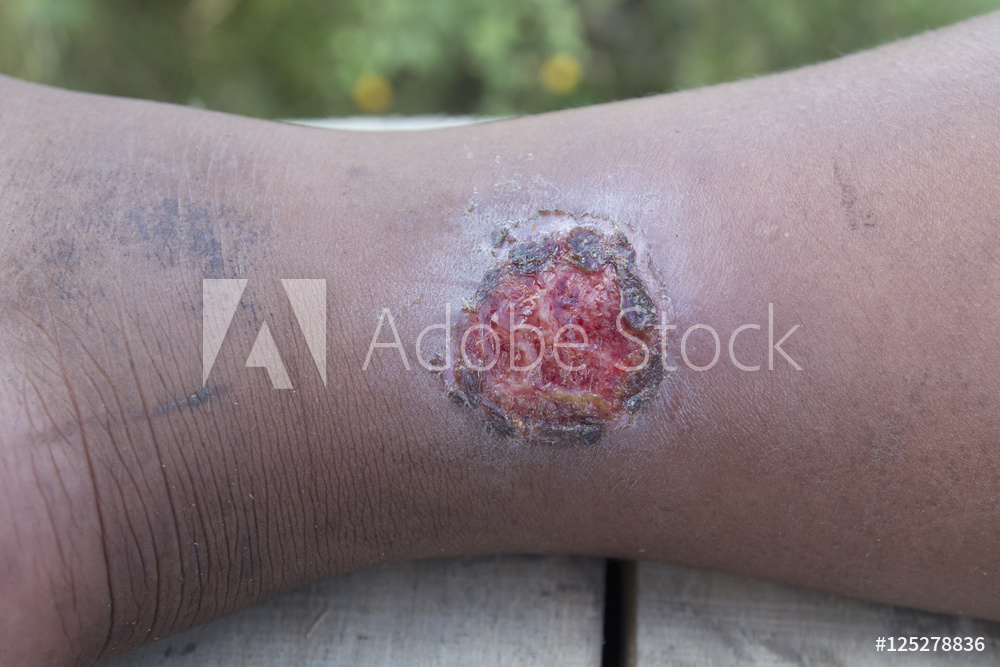
The 43rd chapter of Madhava Nidana is Sadyovrana Nidana which deals with Traumatic Ulcers. Traumatic ulcers are caused by mechanical damage (contact with sharp foodstuff; accidental biting during mastication, talking, or even sleeping) and thermal, electrical, or chemical burns
Chapter 42 – Sharira Vrana Nidanam
The 42nd Chapter of Madhava Nidana is Sharira Vrana Nidanam which deals with Organic Ulcers. An ulcer is a painful sore that is slow to heal and sometimes recurs. Ulcers aren’t uncommon. Why they appear and their corresponding symptoms typically depend on their underlying causes.
Chapter 41 – Vrana Shotha Nidanam
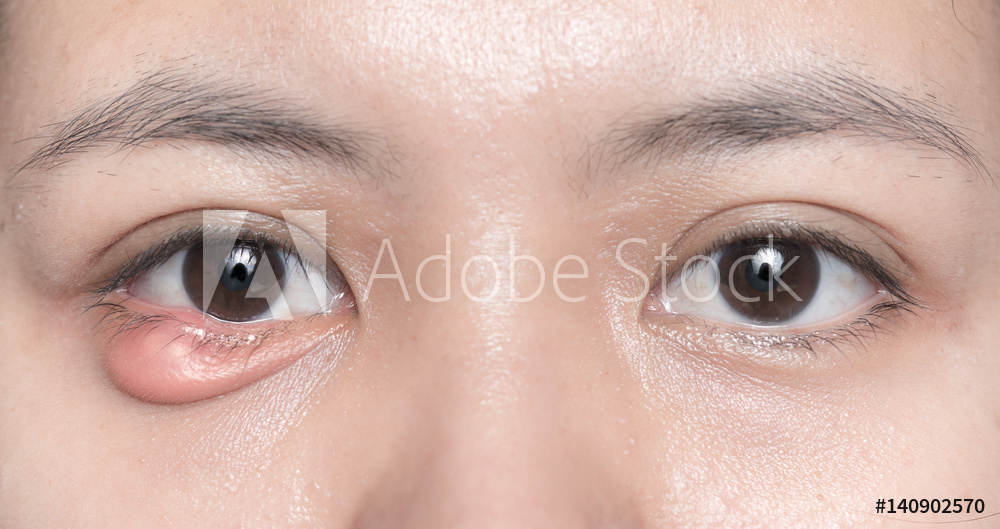
The 41st chapter of Madhava Nidana is Vrana Shotha Nidana which deals with Inflammatory swelling. The swelling process, also known as edema, is the result of acute inflammation, a response triggered by damage to living tissues. In the case of injury, the purpose of the inflammatory response is to remove components of damaged tissue in order to allow the body to begin to heal.
Chapter 40 – Vidradhi Nidanam
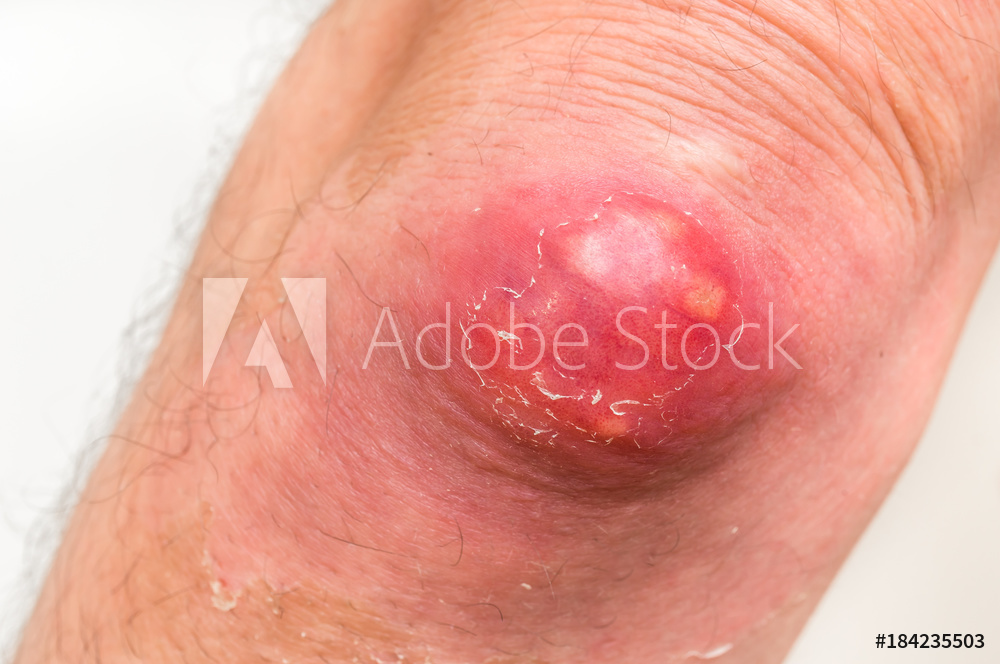
The 40th chapter of Madhava Nidana is Vidradhi Nidana which deals with Abscesses. An abscess is a painful collection of pus, usually caused by a bacterial infection. Abscesses can develop anywhere in the body. A skin abscess often appears as a swollen, pus-filled lump under the surface of the skin. You may also have other symptoms of an infection, such as a high temperature and chills.
Chapter 39 – Shlipada Nidanam
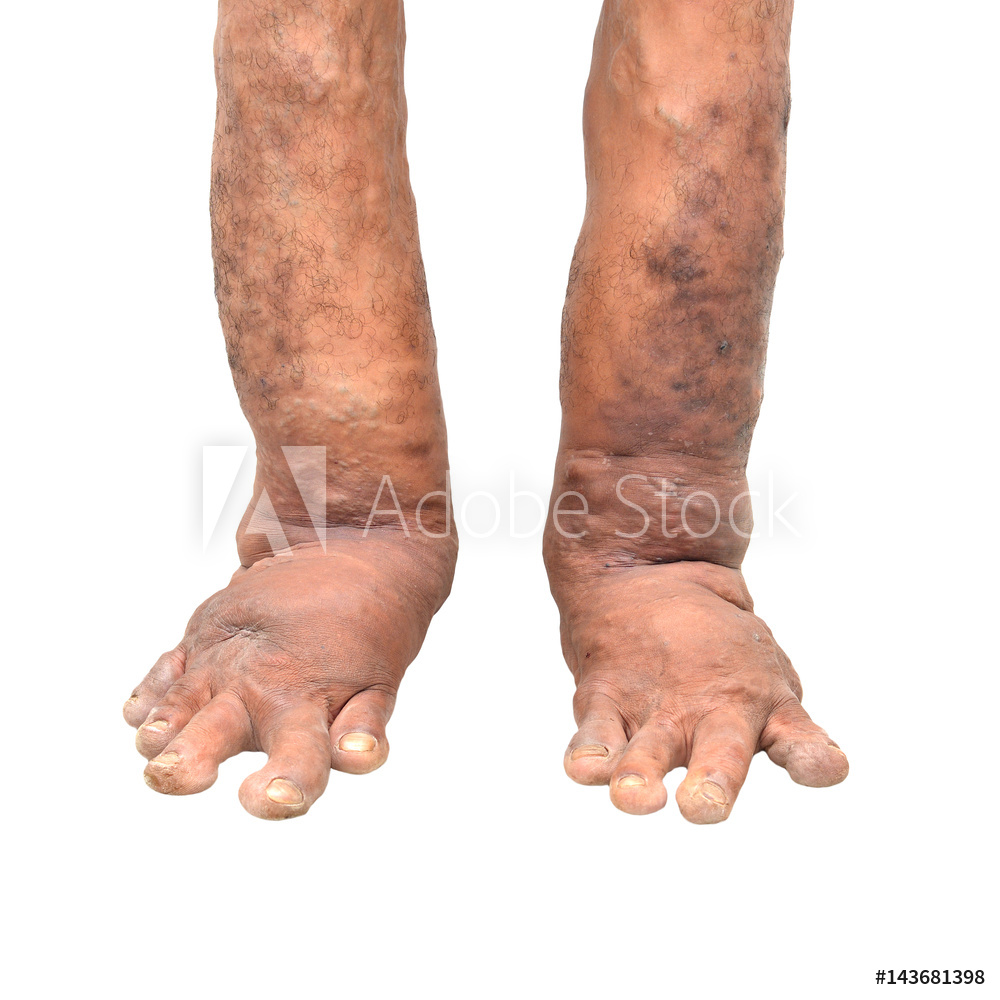
The 39th chapter of Madhava Nidana is Shlipada Nidanam which deals with Filariasis. Filariasis is an infectious tropical disease caused by any one of several thread-like parasitic round worms. The two species of worms most often associated with this disease are Wuchereria bancrofti and Brugia malayi. The larval form of the parasite transmits the disease to humans by the bite of a mosquito.
Chapter 38 – Galaganda – Gandamala – Apachi – Granthi – Arbuda Nidanam
The 38th chapter of Madhava Nidana is Galaganda – Gandamala – Apachi – Granthi – Arbuda Nidanam which deals with Cervical Lymphadenoma, Scrofula – Tumors, Cancer. Cervical lymphadenopathy is abnormal enlargement of lymph nodes (LNs) in the head and neck usually >1 cm